Cybercrime costs Australian businesses billions yearly, with the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) reporting that cybercrime-related losses exceeded $33 billion in 2022. The increasing number of cyberattacks and data breaches makes safeguarding sensitive information one of the most pressing challenges in today’s digital landscape.
Encryption is indispensable for data protection, converting sensitive information into unreadable encrypted data. This ensures that even advanced attackers cannot access it without the correct decryption key. Encryption acts as a shield, protecting data at rest and in transit from unauthorised access.
It secures critical information such as financial records, personal details, and intellectual property, reducing risks and enhancing security. Organisations that prioritise encryption build strong defences against breaches and maintain data confidentiality.
Understanding encryption’s role in today’s digital landscape is vital for mitigating cyber risks. Encryption ensures sensitive information remains secure, even against evolving threats, making it an essential component of modern cybersecurity.
What Is Encryption?
Encryption is vital in data security, ensuring sensitive information remains protected from unauthorised access. Understanding its principles is key to safeguarding personal and financial data.
What is Encryption, and How Does it Work?
Encryption transforms readable information, known as plaintext, into an unreadable format called ciphertext. This process uses encryption algorithms and encryption keys, the foundation for securing data. Without the correct key, decrypting data back into its original form is nearly impossible. This method is crucial in protecting data from threats like data breaches and identity theft.
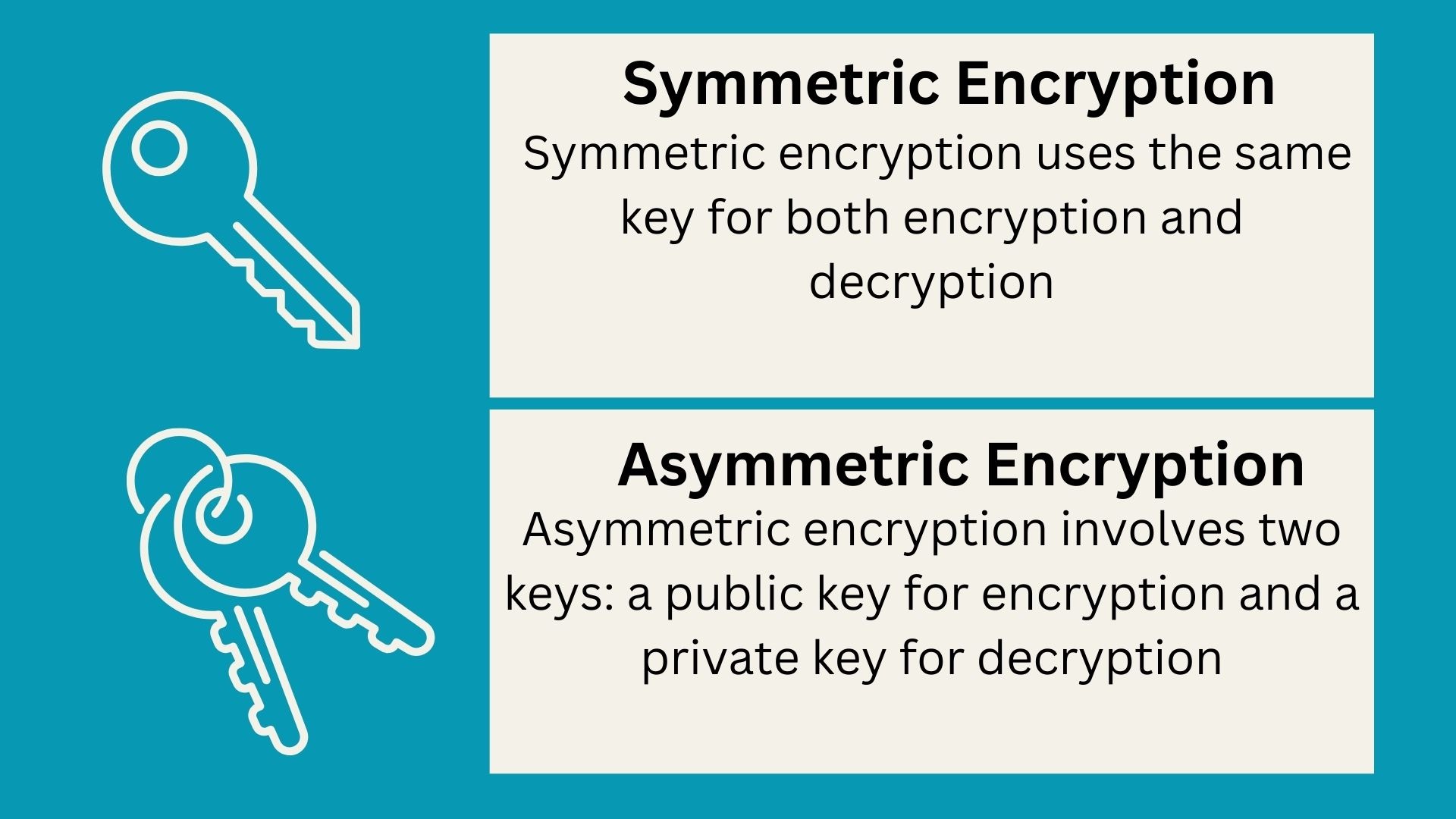
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. It is fast and efficient, making it ideal for large volumes of data. Examples include securing stored financial data or personal files. However, sharing the same key securely between parties can be challenging.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption involves two keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. It is often used in scenarios that require secure communication, such as email encryption or digital signatures. This method offers enhanced security as the private key is never shared, making it highly effective in preventing data breaches.
Encryption, through its various methods and uses, remains an essential tool in the fight to protect data. Understanding the role of encryption and using the right approach ensures sensitive information stays secure.
Common Types of Encryption Algorithms
Encryption plays an essential role in protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. Modern encryption techniques rely on advanced algorithms to secure information and ensure robust data protection.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
The Advanced Encryption Standard is widely regarded for its speed and reliability. It uses symmetric encryption techniques, making it ideal for securing sensitive data in applications like cloud storage and financial transactions. AES is considered a benchmark for modern encryption techniques due to its efficiency and ability to resist common attacks.
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
RSA is a public-key algorithm that uses asymmetric encryption. It encrypts data with a public key and decrypts it with a corresponding decryption key. This makes it an excellent choice for secure communication, such as encrypting emails or verifying digital signatures. RSA is a cornerstone of public-key cryptography and highlights the importance of encryption in maintaining trust online.
Blowfish and Twofish
Blowfish and its successor, Twofish, are symmetric encryption algorithms often used in payment systems and file protection. These algorithms provide strong security while maintaining speed, making them ideal for specific applications requiring quick data encryption.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
ECC is a public-key encryption technique that uses smaller key sizes, making it efficient for mobile and embedded devices. It offers strong security with reduced computational requirements and is critical in environments with limited resources.
Choosing the correct encryption method is crucial to protect sensitive data and meet standards like the General Data Protection Regulation. Each algorithm serves unique purposes, ensuring data remains encrypted and secure against evolving threats.
The Role of Encryption in Safeguarding Sensitive Data
Encryption is a critical tool for safeguarding sensitive information across various scenarios. It ensures data remains secure, even amidst evolving threats.

Data at Rest
Data at rest refers to information stored in databases, cloud environments, or physical devices. Encryption protects this data from unauthorised access or theft. Files, databases, and backups are encrypted to prevent sensitive details like financial records or personal information from being exposed, even if storage systems are compromised. This ensures that stored data is secure against breaches.
Data in Transit
Data in transit covers information being shared or transferred across networks. Encryption secures these communications, such as emails, file transfers, and browsing sessions. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt transmitted data, ensuring it cannot be intercepted or modified during transfer. This is vital for maintaining network confidentiality, especially in online transactions or file sharing.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption ensures only the intended recipients can access the content of communications. This method encrypts data on the sender’s device and only decrypts it on the recipient’s device, leaving no opportunity for interception. Popular messaging platforms use this approach to secure chats, calls, and shared files. This guarantees messages remain private, even if the platform itself is accessed.
Encryption’s role in safeguarding sensitive data is evident across these scenarios. Whether securing stored files, protecting transmitted information, or ensuring private communication, encryption provides a dependable layer of defence.
Industries That Rely on Encryption for Data Security
Encryption is a key component of data security, playing a vital role in protecting sensitive information across various industries in an increasingly digital world.
Finance and Banking
The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) requires financial institutions to implement strict cybersecurity measures under CPS 234. Encryption is a core requirement to protect customer transactions, banking data, and digital payments. Australian banks follow ASIC regulations and RBA guidelines to ensure encrypted financial data remains secure from cyber threats.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry relies heavily on encryption to secure patient data and electronic health records. Encryption ensures that healthcare data, such as medical histories and test results, remains private and protected from breaches.
E-Commerce and Retail
E-commerce platforms and retail businesses use encryption to secure payment systems and protect user data. Sensitive information, including credit card details, is encrypted with a secret key during transactions to prevent unauthorised access. Securing data ensures digital systems remain reliable and customer trust is upheld.
Government and Defence
The Australian Signals Directorate (ASD) and Essential Eight security framework guide encryption standards for the Australian government and defence sectors. Encryption is essential for protecting classified data and preventing unauthorised access to national security systems. Federal and state agencies must comply with the Information Security Manual (ISM).
Legal and Compliance Requirements Driving Encryption
Encryption is a crucial measure for ensuring compliance with various data protection regulations. These legal frameworks highlight the importance of securing sensitive data to avoid breaches and penalties.
Australian Privacy Act & Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) Scheme
The Australian Privacy Act 1988 requires organisations to take reasonable steps to protect personal data from misuse, interference, or unauthorised access. Under the Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) scheme, businesses must report serious data breaches involving personal information. Encryption is considered a best practice to meet compliance obligations, and failure to protect sensitive data can result in penalties of up to $2.5 million.
Health Records Act 2001 & APRA CPS 234
The Health Records Act 2001 (VIC) and state-based health privacy laws regulate handling medical records in Australia. Additionally, APRA CPS 234 requires financial institutions to implement strong security controls, including encryption, to protect sensitive data. Non-compliance can lead to significant fines and regulatory action.
Australian Privacy Act
The Australian Privacy Act expects organisations to take reasonable steps to protect personal data from misuse or unauthorised access. While encryption is not directly mandated, it is considered a best practice for compliance. Serious breaches of privacy obligations under the Act can result in penalties of up to AUD 2.1 million. Implementing encryption demonstrates a commitment to securing personal information.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to severe financial and reputational consequences. Encrypting sensitive data helps organisations meet compliance requirements and avoid penalties. These legal frameworks underline the role of encryption as an essential tool in protecting data and maintaining trust.
Challenges and Misconceptions About Encryption
Encryption remains a critical aspect of data privacy in the digital age, but several challenges and misconceptions surround its use.
Challenges in Implementation
Proper encryption implementation can be complex, especially when ensuring that only authorised parties can access data. Managing the correct key for encryption and decryption requires robust key management practices to prevent unauthorised access. Strong encryption often demands significant computing power, leading to performance trade-offs in specific systems. The costs involved in deploying comparable security measures for financial transactions, healthcare organisations, and trade secrets may also deter small businesses.
Misconceptions About Encryption
A major misconception is that encryption ensures data is foolproof, but vulnerabilities can be exploited without regular updates and secure key management. Another mistaken belief is that encryption is only necessary for large organisations or financial institutions. In reality, protecting data from an unauthorised person is essential for businesses of all sizes. Encryption is also vital for safeguarding digital signatures, ensuring data privacy, and protecting sensitive information in the digital world.
Maintaining Security
Regular updates, proper implementation, and secure storage of the secret code used in asymmetric methods are all vital. These steps keep data safe and ensure encryption remains effective in preventing breaches. In today’s digital age, encryption and decryption practices are critical for protecting sensitive information against evolving threats.
Fortify Your Digital Defences with Encryption
Protecting sensitive information is essential in today’s digital age. Encryption ensures data privacy, safeguarding financial transactions, trade secrets, and personal information from unauthorised access. Strong encryption is critical to maintaining security in an evolving threat landscape.
Taking proactive steps to secure data is vital for businesses. Proper implementation of encryption, regular system updates, and secure key management are necessary to keep information safe. Organisations across industries, including healthcare and financial institutions, rely on robust encryption strategies to prevent breaches and maintain trust.
Our team provides tailored cybersecurity solutions to meet the unique needs of Australian businesses. We implement industry-leading encryption strategies to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with Australian cybersecurity regulations. Whether securing financial data, healthcare records, or corporate communications, we help businesses fortify their digital defences.
Contact Datcom today for expert advice and customised encryption solutions to protect your business from evolving cyber threats.




